Enhancing Sustainability of the Transboundary Cambodia–Mekong Delta Aquifer (CMDA): Vietnam and Cambodia
1. Overview
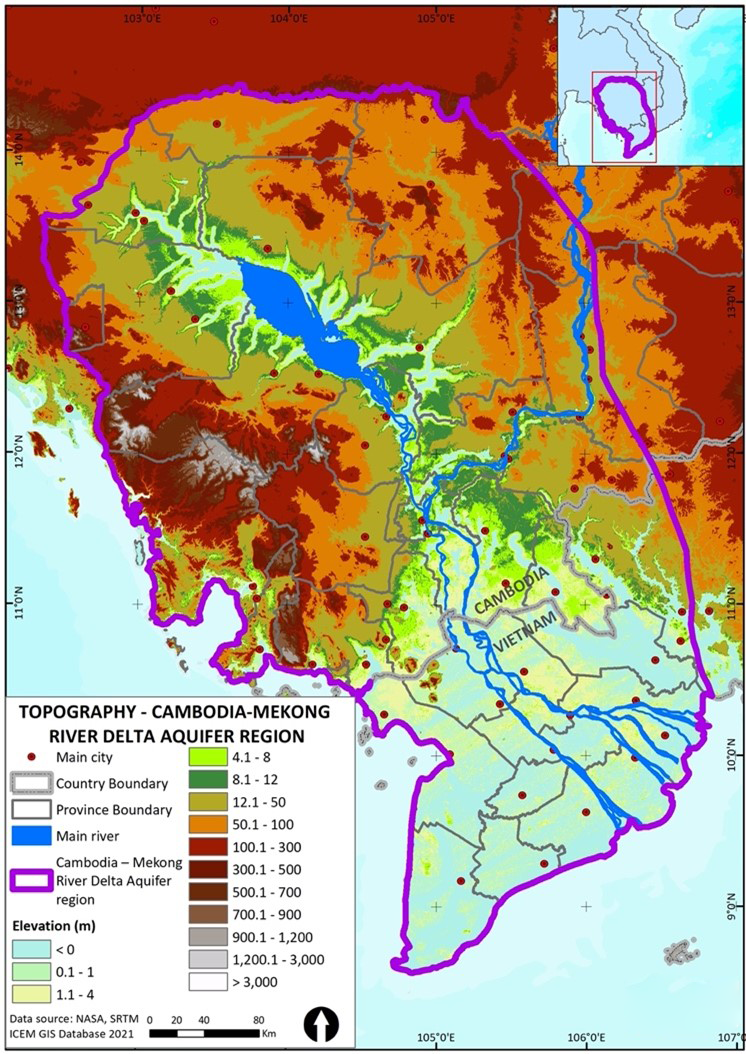
The Cambodia–Mekong River Delta Aquifer (CMDA) is one of the most important shared groundwater systems in Southeast Asia. Lying beneath Cambodia’s floodplains and the Mekong Delta of Vietnam, the aquifer sustains millions of people with water for drinking, farming, and ecosystems. Yet this hidden resource is under increasing stress from over-extraction, salinity intrusion, and climate change.
Enhancing the Sustainability of the Transboundary Cambodia-Mekong Delta Aquifer is the first initiative of its kind in the Lower Mekong Basin. Running from 2024 to 2028, it aims to strengthen the sustainability of this shared aquifer through science-based knowledge, cooperative governance, and inclusive participation. Funded by the Global Environment Facility (GEF), implemented by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), and executed by IUCN, the project is co-owned by the Governments of Cambodia and Vietnam.
2. Our Goal
To strengthen environmental sustainability and water security in the Lower Mekong Basin by focusing on improved governance and sustainable utilization of the Cambodia-Mekong River Delta Transboundary Aquifer.
The CMDA project is designed to deliver both knowledge and cooperation to reach its goal through five interlinked objectives:
- Strengthen groundwater governance between Cambodia and Vietnam through joint mechanisms and dialogue.
- Build science and knowledge by carrying out a Transboundary Diagnostic Analysis (TDA) to identify key pressures and risks.
- Agree on a Strategic Action Programme (SAP) endorsed by both governments, that outlines practical and coordinated responses.
- Promote inclusive participation by ensuring that women, Indigenous Peoples, and ethnic minorities are fully engaged.
- Support resilience and sustainability in the Mekong Delta through policies, practices, and community action.
3. Why Groundwater Matters
Groundwater in the CMDA system is essential for daily life and national economies. It provides safe drinking water for millions of rural and urban households, sustains irrigated agriculture in one of the world’s most productive deltas, and supports wetlands and biodiversity.
But the aquifer is at risk. Unsustainable extraction is leading to land subsidence, saline intrusion is threatening freshwater supplies, and climate change is altering rainfall and recharge patterns. Without action, the very foundation of water security in the delta will be undermined.
4. Key Project Facts
-
Duration: 2024–2028.
-
Countries: Cambodia & Vietnam.
-
Partners: Ministry of Environment (Cambodia), Ministry of Agriculture and Environment (Viet Nam)/ Department of Water Resources Management (Vietnam).
-
Executing Partners: UNESCO, WWAP – UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme and MERFI
-
Funding: GEF International Water



 The Cambodia–Mekong River Delta Aquifer (CMDA) Project is a Global Environment Facility (GEF) International Waters initiative implemented by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and led by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as Lead Executing Agency, with UNESCO and MERFI as Executing Partners, in collaboration with the Governments of Viet Nam and Cambodia.
The Cambodia–Mekong River Delta Aquifer (CMDA) Project is a Global Environment Facility (GEF) International Waters initiative implemented by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and led by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as Lead Executing Agency, with UNESCO and MERFI as Executing Partners, in collaboration with the Governments of Viet Nam and Cambodia.